|
| Eiko Ishioka |
La terza parte del
post a puntate dedicato alle diverse
fasi che caratterizzano il modello base del processo progettuale, partendo dal
momento in cui nasce l’idea fino a quando la collezione sarà presentata ai
buyer, alla stampa e al pubblico
post a puntate dedicato alle diverse
fasi che caratterizzano il modello base del processo progettuale, partendo dal
momento in cui nasce l’idea fino a quando la collezione sarà presentata ai
buyer, alla stampa e al pubblico
The third part of the post in episodes dedicated to the different stages that characterize the basic model of the design process, starting from the moment when the idea was born until the collection will be presented to buyers, the press and the public
Nelle puntate precedenti abbiamo visto la fase più
concettuale (che potete trovare qui) e quella di progettazione (che potete
trovare qui), i due momenti in cui la fantasia dello stilista viene lasciata
più libera di creare. Oggi invece vorrei analizzare la fase in cui tutte le
ispirazioni e i pensieri si concretizzano in qualcosa di tangibile, in quello
che diventerà un prodotto destinato alla vendita o un “pezzo d’arte
indossabile”
concettuale (che potete trovare qui) e quella di progettazione (che potete
trovare qui), i due momenti in cui la fantasia dello stilista viene lasciata
più libera di creare. Oggi invece vorrei analizzare la fase in cui tutte le
ispirazioni e i pensieri si concretizzano in qualcosa di tangibile, in quello
che diventerà un prodotto destinato alla vendita o un “pezzo d’arte
indossabile”
In previous episodes we have seen the conceptual stage (you can find here) and that of design (which you can find here), the two moments in which the imagination of the designer is left more free to create. But today I would like to analyze the stage where all the inspirations and thoughts materialize into something tangible, in what will become a product for sale or a “piece of wearable art“
Questo è il momento in cui le idee dello stilista iniziano a
prendere forma, in cui si valuta l’intero progetto non più solo in modo
teorico, ma con un riscontro pratico.
prendere forma, in cui si valuta l’intero progetto non più solo in modo
teorico, ma con un riscontro pratico.
Per quasi tutti gli atelier del mondo questa fase è
caratterizzata da momenti alternanti di euforia e scoramento. Infatti un gran
numero di capi non vedrà la luce, per problematiche tecniche o estetiche. Si
calcola che i marchi più importanti arrivino a scartare anche il 50% dei
prototipi, mentre la maggior parte delle Maison si attesti intorno al 30% di
“scarti”, mentre soltanto gli atelier più piccoli, solitamente già gravati da
una situazione economica difficile, siano più attenti e riescano ad eliminare
soltanto un 10% dei prototipi.
caratterizzata da momenti alternanti di euforia e scoramento. Infatti un gran
numero di capi non vedrà la luce, per problematiche tecniche o estetiche. Si
calcola che i marchi più importanti arrivino a scartare anche il 50% dei
prototipi, mentre la maggior parte delle Maison si attesti intorno al 30% di
“scarti”, mentre soltanto gli atelier più piccoli, solitamente già gravati da
una situazione economica difficile, siano più attenti e riescano ad eliminare
soltanto un 10% dei prototipi.
This is the moment in which the designer’s ideas begin to take shape, in which it is evaluated the whole project not only theoretically, but with a practical response.
For nearly all of the world atelier this stage is characterized by alternating moments of euphoria and dejection. In fact a large number of animals not see the light, for technical or aesthetic problems. It is estimated that the major brands also come to discard 50% of prototypes, while most of the Maison to be around 30% of “waste“, while only smaller atelier, usually already burdened by a difficult economic situation, are more alert and are able to eliminate only 10% of the prototypes.
 |
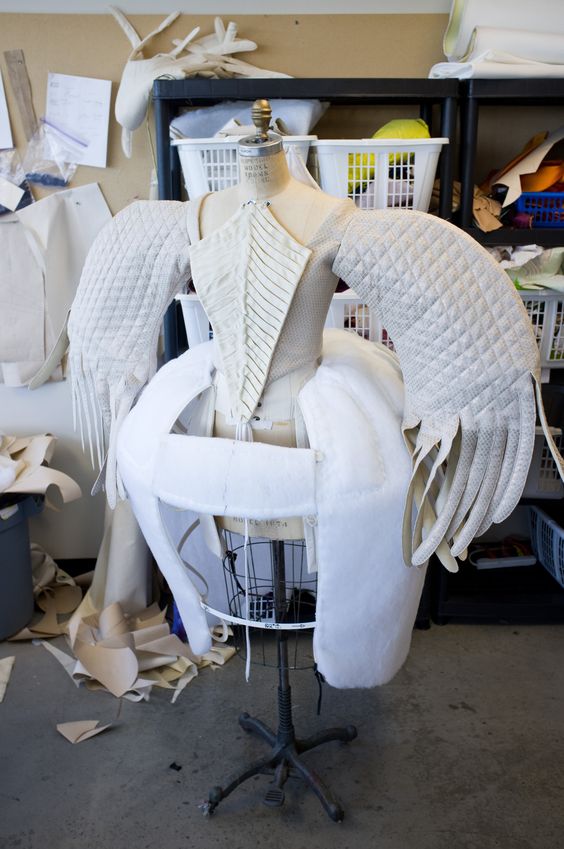
| Changing the prototype, by Han Gu |
I disegni giungono nelle mani del reparto modellistica, dove
vengono analizzati per cercare di capire la vestibilità e le caratteristiche
tecniche da riprodurre sul cartamodello in carta. Questa parte del lavoro è
estremamente delicata, poiché un errore o una cattiva interpretazione delle
indicazioni, ma anche indicazioni poco accurate da parte dell’ufficio
stilistico, possono generare un modello non corrispondente alle volontà e alla
fantasia dello stilista. In questo momento è fondamentale una collaborazione
stretta tra i due reparti, un continuo scambio di opinioni. Spesso infatti,
alcuni suggerimenti cruciali seguono un percorso inverso: l’esperienza del
modellista aiuta il designer a creare modelli più facilmente realizzabili o a
risolvere alcune problematiche tecniche legate alla costruzione del capo.
vengono analizzati per cercare di capire la vestibilità e le caratteristiche
tecniche da riprodurre sul cartamodello in carta. Questa parte del lavoro è
estremamente delicata, poiché un errore o una cattiva interpretazione delle
indicazioni, ma anche indicazioni poco accurate da parte dell’ufficio
stilistico, possono generare un modello non corrispondente alle volontà e alla
fantasia dello stilista. In questo momento è fondamentale una collaborazione
stretta tra i due reparti, un continuo scambio di opinioni. Spesso infatti,
alcuni suggerimenti cruciali seguono un percorso inverso: l’esperienza del
modellista aiuta il designer a creare modelli più facilmente realizzabili o a
risolvere alcune problematiche tecniche legate alla costruzione del capo.
The drawings come in the hands of the modeling department, where they are analyzed to try to understand the fit and specifications to reproduce on the pattern made of paper. This part of the work is extremely delicate, because a mistake or a bad interpretation of the indications, but also inaccurate indications by the style team, can generate a model that does not match to the will and the imagination of the designer. Right now is essential a close collaboration between the two departments, a continuous exchange of views. Often, some crucial suggestions follow a reverse path: the experience patternmaker helps the designers to create more feasible models or to solve some technical problems related to the construction of the garment.
 |
| My work table |
Una volta che il cartamodello è stato realizzato, la
collezione procede nel suo percorso con la realizzazione dei primi prototipi
tagliati e cuciti in una leggera stoffa di cotone, chiamata telina e vengono
provati su manichino o modella per poter essere “sdifettati”. Anche questa
operazione richiede grande attenzione da parte dello stilista, che dovrà
supervisionare con la prémiere (capo modellista) la struttura dei modelli e
togliere ogni difetto di vestibilità: esaminare pinces e tagli, controllare le
lunghezze e le larghezze, definire i dettagli e l’aspetto generale dell’abito.
collezione procede nel suo percorso con la realizzazione dei primi prototipi
tagliati e cuciti in una leggera stoffa di cotone, chiamata telina e vengono
provati su manichino o modella per poter essere “sdifettati”. Anche questa
operazione richiede grande attenzione da parte dello stilista, che dovrà
supervisionare con la prémiere (capo modellista) la struttura dei modelli e
togliere ogni difetto di vestibilità: esaminare pinces e tagli, controllare le
lunghezze e le larghezze, definire i dettagli e l’aspetto generale dell’abito.
Once the pattern has been realized, the collection proceeds in its path with the realization of the first prototypes cut and sewn into a light cotton fabric, called muslin, and are tested on a mannequin or a live model to remove the defects. This operation requires great care by the designer, who will oversee with the prémiere (head pattern maker) the structure of the models and remove any defect of wearability: look darts and cuts, check the lengths and widths, define the details and the general appearance of clothes.
 |
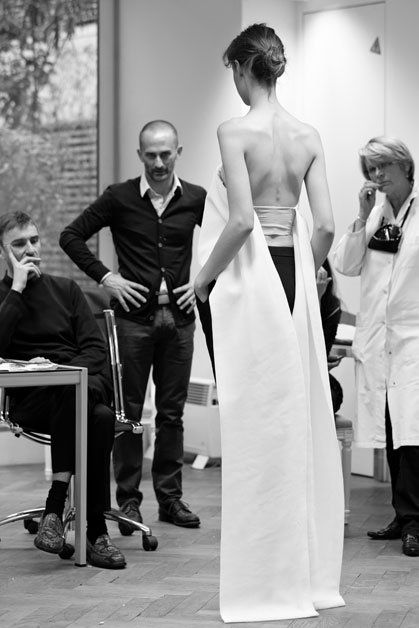
| Dior Haute Couture AW15 |
Normalmente queste operazioni vanno ripetute fintanto che
tutti i modelli della collezione siano pronti per essere provati con le stoffe
decise in fase di progettazione. Per le Maison di moda di medie e grandi
dimensioni queste prove precedono la realizzazione del campionario vero e
proprio. L’ufficio prodotto si occupa di acquistare piccoli quantitativi delle
stoffe scelte in modo che lo stilista possa valutare l’efficacia dei modelli
ancora in fase di prova. Atelier più piccoli, sempre alle prese con
ristrettezze di budget e mille incombenze a carico di un personale decisamente
più ridotto, passano direttamente alla realizzazione del campionario soltanto
dopo aver effettuato diverse prove in telina.
tutti i modelli della collezione siano pronti per essere provati con le stoffe
decise in fase di progettazione. Per le Maison di moda di medie e grandi
dimensioni queste prove precedono la realizzazione del campionario vero e
proprio. L’ufficio prodotto si occupa di acquistare piccoli quantitativi delle
stoffe scelte in modo che lo stilista possa valutare l’efficacia dei modelli
ancora in fase di prova. Atelier più piccoli, sempre alle prese con
ristrettezze di budget e mille incombenze a carico di un personale decisamente
più ridotto, passano direttamente alla realizzazione del campionario soltanto
dopo aver effettuato diverse prove in telina.
Normally these operations are repeated until all of the collection’s models are ready to be tested with the fabrics decided at the design stage. For medium and large fashion Maison these tests precede the realization of the actual sampling. The product office deals with purchase small quantities of the fabrics chosen so that the designer can assess the effectiveness of the models still under test. Smaller atelier, always struggling with budget constraints and a thousand tasks borne by a significantly smaller staff, pass directly to the manufacture of samples only after carrying out various tests in muslin.
 |
| Thom Browne | The design team begins to furiously apply even more details to the dress |
Questi sono i momenti che caratterizzano la fase di
prototipazione
prototipazione
These are the moments that characterize the stage of prototyping
1
REALIZZAZIONE DEI CARTAMODELLI: sulla base delle
indicazioni contenute nella scheda tecnica e nel disegno in piatto vengono
realizzati i cartamodelli cartacei di tutti i capi della collezione; la
première, ovvero la modellista responsabile del suo reparto, è una figura
fondamentale dell’azienda, perché attraverso la sua capacità di interpretazione
del modello sarà possibile rendere tridimensionale la proposta dello stilista
indicazioni contenute nella scheda tecnica e nel disegno in piatto vengono
realizzati i cartamodelli cartacei di tutti i capi della collezione; la
première, ovvero la modellista responsabile del suo reparto, è una figura
fondamentale dell’azienda, perché attraverso la sua capacità di interpretazione
del modello sarà possibile rendere tridimensionale la proposta dello stilista
CONSTRUCTION OF PATTERNS: based on the indications contained in the tech-pack and drawing are made paper patterns of all the garments in the collection; the prémiere, which is the pattern maker responsible for her department, is a key figure in the company, because through her capabilities on interpretation of the model it will be able to to make three-dimensional the designer proposal
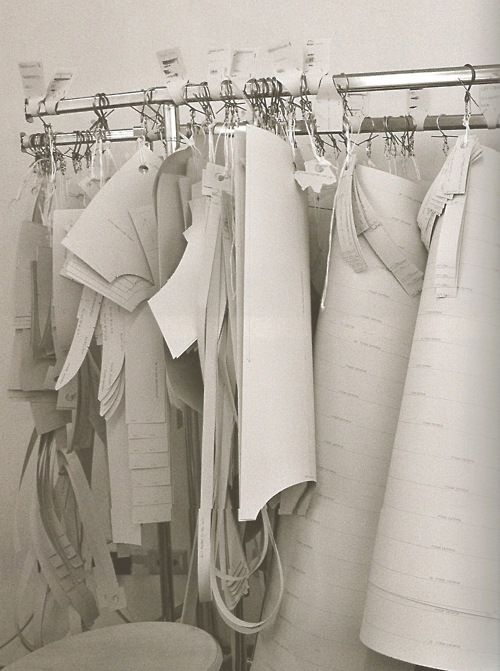 |
| Prada dress patterns |
2
PROVA IN TELINA: prima di realizzare un prototipo vero
e proprio coni tessuti definitivi, il
cartamodello viene tagliato e cucito in una stoffa di cotone leggero o in un
tessuto similare al definitivo ma più economico, in modo da poter subire
modifiche senza essere troppo oneroso economicamente
e proprio coni tessuti definitivi, il
cartamodello viene tagliato e cucito in una stoffa di cotone leggero o in un
tessuto similare al definitivo ma più economico, in modo da poter subire
modifiche senza essere troppo oneroso economicamente
TEST IN MUSLIN: before realizing a real and precise prototype with the final fabrics, the pattern is cut and sewn in a light cotton fabric or a fabric similar to the final but cheaper, so that it can undergo modifications without being too onerous economically
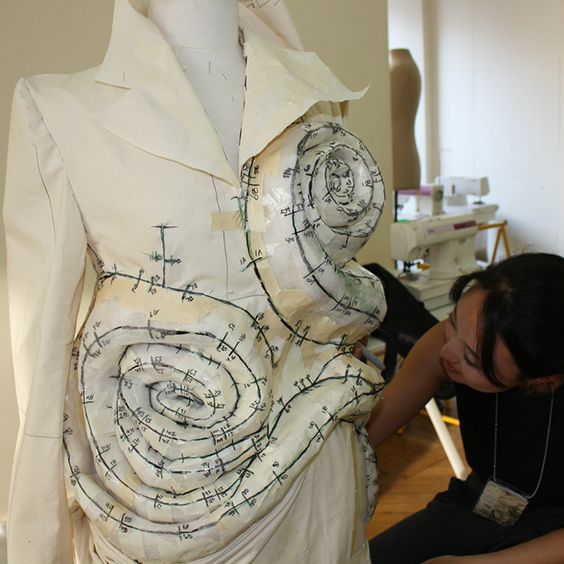 |
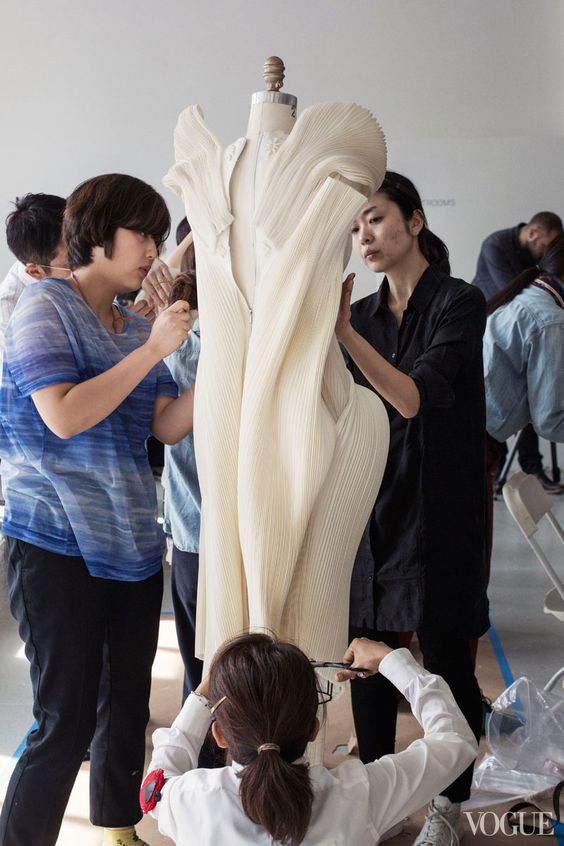
| 3D sculptural fashion design development |
3
SDIFETTAMENTO E RIFINITURA DEI MODELLI: i prototipi in telina
vengono provati su una modella in taglia standard (in base al target di
clientela del brand) e vengono tolti i difetti di vestibilità o estetici
fintanto che il il modello non corrisponda esattamente e perfettamente al
desiderio dello stilista; spesso i capi subiscono tante modificazioni da
rendere necessarie più prove
vengono provati su una modella in taglia standard (in base al target di
clientela del brand) e vengono tolti i difetti di vestibilità o estetici
fintanto che il il modello non corrisponda esattamente e perfettamente al
desiderio dello stilista; spesso i capi subiscono tante modificazioni da
rendere necessarie più prove
REMOVING DEFECTS AND FINISHING OF MODELS: prototypes in muslin are tested on a fashion model in standard size (based on the brand’s target customers) and the fit or aesthetic defects are removed until that the garment does not correspond exactly and perfectly to desire of the designer; often the clothes undergo such modification as to make necessary more tests
 |
| Men’s haute couture garment construction by Francesco Smalto |
4
ACQUISTO DEL MATERIALE PER IL CAMPIONARIO: per poter
realizzare il campionario definitivo l’ufficio prodotto ha acquistato dai vari
fornitori un quantitativo ridotto di stoffe e accessori in misura strettamente
necessaria alla creazione di un singolo capo o di qualche ripetizione dei
modelli (a seconda del budget a disposizione)
realizzare il campionario definitivo l’ufficio prodotto ha acquistato dai vari
fornitori un quantitativo ridotto di stoffe e accessori in misura strettamente
necessaria alla creazione di un singolo capo o di qualche ripetizione dei
modelli (a seconda del budget a disposizione)
PURCHASE OF MATERIAL FOR THE SAMPLES: in order to realize the final sampling the product office purchased from various suppliers a reduced quantity of fabrics and accessories in a strictly necessary measure for the creation of a single garment or some repetition of models (depending on budget available)
 |
| Nelly Saunier featherwork atelier |
5
REALIZZAZIONE DEI PROTOTIPI DEFINITIVI: sulla base delle
modifiche effettuate nelle prove in telina, vengono alla fine realizzati i capi
prototipi definitivi che finalmente avranno le stoffe e i colori a
loro attribuiti in fase di progettazione; in questo modo lo stilista potrà
avere un’idea più precisa della vera caduta della stoffa, del movimento
dell’abito, della vestibilità e dell’armonia dell’insieme, ed eventualmente
poter effettuare ulteriori modifiche
modifiche effettuate nelle prove in telina, vengono alla fine realizzati i capi
prototipi definitivi che finalmente avranno le stoffe e i colori a
loro attribuiti in fase di progettazione; in questo modo lo stilista potrà
avere un’idea più precisa della vera caduta della stoffa, del movimento
dell’abito, della vestibilità e dell’armonia dell’insieme, ed eventualmente
poter effettuare ulteriori modifiche
REALIZATION OF DEFINITIVE PROTOTYPE : based on changes in the tests made in muslin, at the end the final prototypes are realized and finally will have the fabrics and colors assigned to them in the design phase; in this way the designer can get a better idea of the true fall of the fabric, the garment movement, fit and harmony of the whole, and possibly be able to make further changes
VI ASPETTO LA PROSSIMA SETTIMANA CON LA QUARTA E ULTIMA PUNTATA DI QUESTO POST DEDICATO ALLE VARIE FASI DEL PROCESSO PROGETTUALE
I’LL WAIT YOU NEXT WEEK WITH THE FOURTH AND LAST EPISODE OF THIS POST DEDICATED TO THE VARIOUS PHASES OF DESIGN PROCESS